前端面试手写题集合
0. promise 执行过程
js
console.log('scriot start')
async function async1() {
await async2()
console.log('async1 end');
}
async function async2() {
console.log('async2 end');
}
async1()
setTimeout(function() {
console.log('setTimeout')
}, 0)
new Promise(resolve => {
console.log('Promise')
resolve()
})
.then(function () {
console.log('promise1')
})
.then(function() {
console.log('promise2')
})
console.log('script end')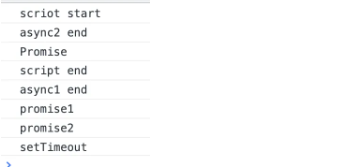
0.1 手写PromiseAll方法
https://juejin.cn/post/7069805387490263047#heading-5
js
Promise.MyAll = (promises)=>{
let arr = [];
let count = 0;
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
promises.forEach((item, i) => {
Promise.resolve(item).then(res=>{
arr[i] = res
count +=1
if (count === promises.length) {
resolve(arr)
}
}).catch(reject)
});
})
}
const p1 = Promise.resolve('p1')
const p2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('p2 延时一秒')
}, 1000)
})
const p3 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('p3 延时两秒')
}, 2000)
})
const p4 = Promise.reject('p4 rejected')
Promise.MyAll([p1, p2, p3, p4])
.then(res => {
console.log(res)
})
.catch(err => console.log(err)) // p4 rejected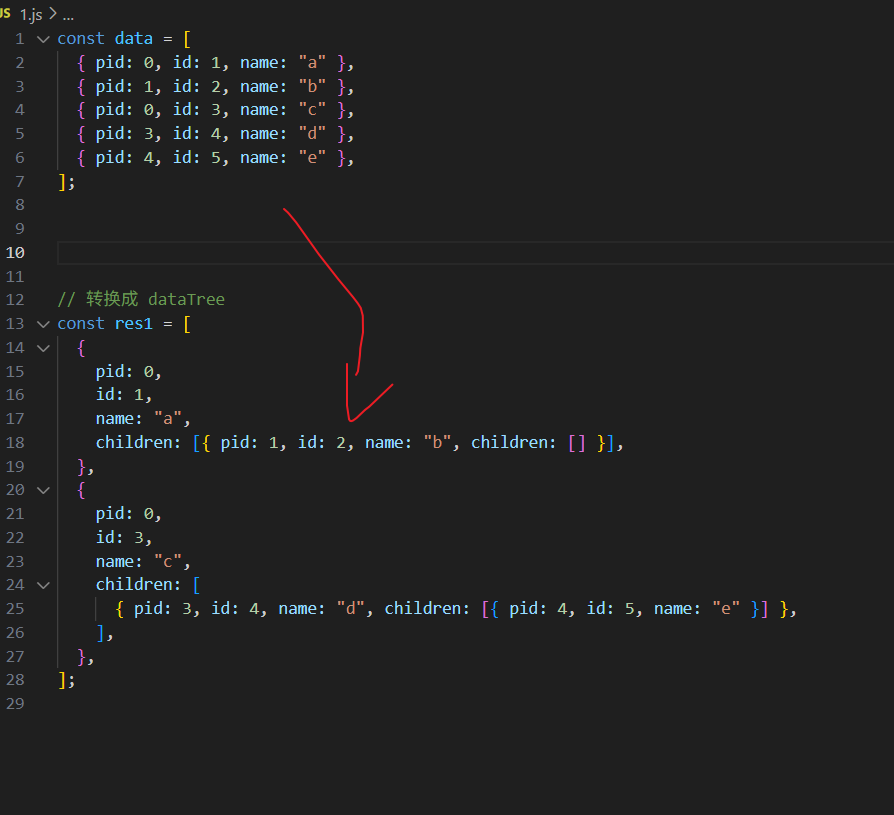
a. 数据结构转换问题
js
const data = [
{ pid: 0, id: 1, name: "a" },
{ pid: 1, id: 2, name: "b" },
{ pid: 0, id: 3, name: "c" },
{ pid: 3, id: 4, name: "d" },
{ pid: 4, id: 5, name: "e" },
];
function formatDataTree(items) {
let res = [];
const getChildren = (res, pid) => {
for (const i of items) {
if (i.pid === pid) {
const newItem = { ...i, children: [] };
res.push(newItem);
getChildren(newItem.children, newItem.id);
}
}
};
getChildren(res, 0);
return res;
}
console.log(formatDataTree(data));
// 转换成 dataTree
const res1 = [
{
pid: 0,
id: 1,
name: "a",
children: [{ pid: 1, id: 2, name: "b", children: [] }],
},
{
pid: 0,
id: 3,
name: "c",
children: [
{ pid: 3, id: 4, name: "d", children: [{ pid: 4, id: 5, name: "e" }] },
],
},
];0. 实现 lazy 链式调用 :
person.eat().sleep(2).eat()
js
// 函数的链式调用1. 实现 find 方法,根据 id 查找 data 树中的任意一项
js
// 实现find方法,根据id 查找data树中的任意一项
const data = [
{
id: "1000",
name: "深圳",
children: [
{
id: "1001",
name: "宝安区",
},
{
id: "1002",
name: "南山区",
},
],
},
{
id: "2000",
name: "广州",
children: [
{
id: "2001",
name: "越秀区",
children: [
{
id: "2002",
name: "大东街道办事处",
},
],
},
{
id: "2003",
name: "荔湾区",
},
],
},
];
const find = (data, id) => {
for (let item of data) {
if (item.id === id) {
return item.name;
}
if (item.children?.length) {
const res = find(item.children, id);
if (res && res !== "未找到") {
return res;
}
}
}
return "未找到";
};
const r1 = find(data, "1000"); // 深圳
const r2 = find(data, "1001"); // 宝安区
const r3 = find(data, "2001"); // 越秀区
const r4 = find(data, "2002"); // 大东街道办事处
const r5 = find(data, "3003"); // 未找到
console.log(r1);
console.log(r2);
console.log(r3);
console.log(r4);
console.log(r5);链式调用函数的方式, 进行加减乘除运算
js
// 链式调用函数的方式, 进行加减乘除运算
class MyCalculator {
constructor(number) {
this.number = number;
}
add(num) {
this.number = this.number + num;
return this;
}
minus(num) {
this.number = this.number - num;
return this;
}
multi(num) {
this.number = this.number * num;
return this;
}
div(num) {
this.number = this.number / num;
return this;
}
toString() {
// 比较时候会触发隐式转换,需要自定义toString方法进行输出
return this.number;
}
}
const calculator = new MyCalculator(121);
if (calculator.add(1).minus(2).multi(3).div(4) == 90) {
console.log("恭喜, 回答正确");
}1. 发布订阅模式
js
2. 防抖函数
js
const func = function (e) {
// @TODO
console.log(e.target.value);
rederCity(this.value);
};
const debounce = function (func, wait) {
let timerId;
return function (...args) {
let _this = this;
clearTimeout(timerId);
timerId = setTimeout(() => {
func.apply(_this, args);
}, wait);
};
};
const debounceFunc = debounce(func, 500);
document.getElementById("search-input").addEventListener("input", debounceFunc);3. 节流函数
js
const func = function (e) {
console.log("timeupdate触发");
console.log("e:", e);
localStorage.setItem("currentTime", this.currentTime);
};
function throttle(func, wait = 0) {
// TODO
let timeId;
return function (...args) {
let _this = this;
if (timeId) {
return;
}
timeId = setTimeout(() => {
func.apply(_this, args);
timeId = undefined;
}, wait);
};
}
const throttleFn = throttle(func, 1000);
video.addEventListener("timeupdate", throttleFn);4. 数组去重
方法一:使用 Set
js
function uniqueArray(arr) {
// @TODO
return [...new Set(arr)];
}方法二:使用 filter
js
function uniqueArray(arr) {
// @TODO
return arr.filter((item, index, self) => {
return self.indexOf(item) === index;
});
}方法三:使用 reduce
js
function uniqueArray(arr) {
// @TODO
return arr.reduce((prev, curr) => {
return prev.includes(curr) ? prev : [...prev, curr];
}, []);
}4.1 实现数组的 myMap 方法
js
Array.prototype.myMap = function (fn, ctx) {
let ret = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
ret.push(fn.call(ctx, this[i], i, this));
}
return ret;
};
// 测试代码
const nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(
"Map:",
nums.myMap((x) => x * 2),
[1, 2]
);4.2 实现数组的 myFilter 方法
js
Array.prototype.myFilter = function (fn, ctx) {
let ret = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
const ret1 = fn.call(ctx, this[i], i, this);
if (ret1) {
ret.push(this[i]);
}
}
return ret;
};
// 测试代码
const nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
console.log(
"Filter:",
nums.myFilter((x) => x > 2)
);5. 数组扁平化
js
function flatten(arr) {
// @TODO
const result = [];
function flat(arr) {
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (Array.isArray(arr[i])) {
flat(arr[i]);
} else {
result.push(arr[i]);
}
}
}
flat(arr);
return result;
}
// 简化版本
function flattenES6(arr) {
return arr.flat(Infinity);
}6. 手写 Promise.all
js
Promise.myAll = function (promises) {
// @TODO
};7. 手写 Promise.allSettled
js
Promise.myAllSettled = function (promises) {
// @TODO
};8. 手写 call 方法
js
const person = {
name: "张三",
age: 18,
sex: "男",
};
Function.prototype.myCall = function (context = window, ...args) {
// @TODO
const key = Symbol();
context[key] = this;
const res = context[key](...args);
delete context[key];
return res;
};
const res = func.myCall(person, 10, 20);
console.log("res 返回值:", res);9. 手写 apply 方法
与myCall方法一致,只是参数不同
js
Function.prototype.myApply = function (context = window, args = []) {
// @TODO
const key = Symbol();
context[key] = this;
const res = context[key](...args);
delete context[key];
return res;
};10. 手写 bind 方法
js
// 1. 定义myBind方法
// 2. 返回绑定this的新函数
// 3. 合并绑定和新传入的参数
Function.prototype.myBind = function (context = window, ...args1) {
// @TODO
return (...regsArgs) => this.call(context, ...args1, ...regsArgs);
};
const bindFunc1 = func1.myBind(person, 10, 20);
const res1 = bindFunc1(30);
console.log("res1 返回值:", res1);apply实现
js
Function.prototype.myBind = function (context = window, ...args1) {
// @TODO
return (...regsArgs) => this.apply(context, [...args1, ...regsArgs]);
};
// 调用并获取返回值
const bindFunc1 = func1.myBind(person, 10, 20);
const res1 = bindFunc1(30);
console.log("res1 返回值:", res1);11. 手写 new 操作符
js
function myNew(constructor, ...args) {
// @TODO
}12. 手写 instanceof
js
function myInstanceof(obj, constructor) {
// @TODO
}13. 函数柯里化
将多个参数的函数,转换为单个参数的函数
js
function curriedAdd(a) {
// @TODO
return function (b) {
return function (c) {
return a + b + c;
};
};
}
console.log(curriedAdd(1)(2)(3)); // 6js
// 需求: 改写函数,实现如下效果
// 思路:
// 1. 保存不定长参数 array
// 2. 是否达到长度
// 3. 累加5个参数, 返回函数
let nums = [];
function sum(...args) {
// @TODO
nums.push(...args);
if (nums.length >= 5) {
const res = nums.slice(0, 5).reduce((p, v) => p + v, 0);
nums = []; // 注意累加之后需要清空数组,保证下次累加的值是正确的
return res;
} else {
return sum;
}
}
// 使用示例
function sum(a, b, c, d, e) {
return a + b + c + d + e;
}
sum(1)(2)(3)(4)(5);
sum(1)(2, 3)(4)(5);
sum(1)(2, 3, 4)(5);
sum(1, 2, 3)(4, 5);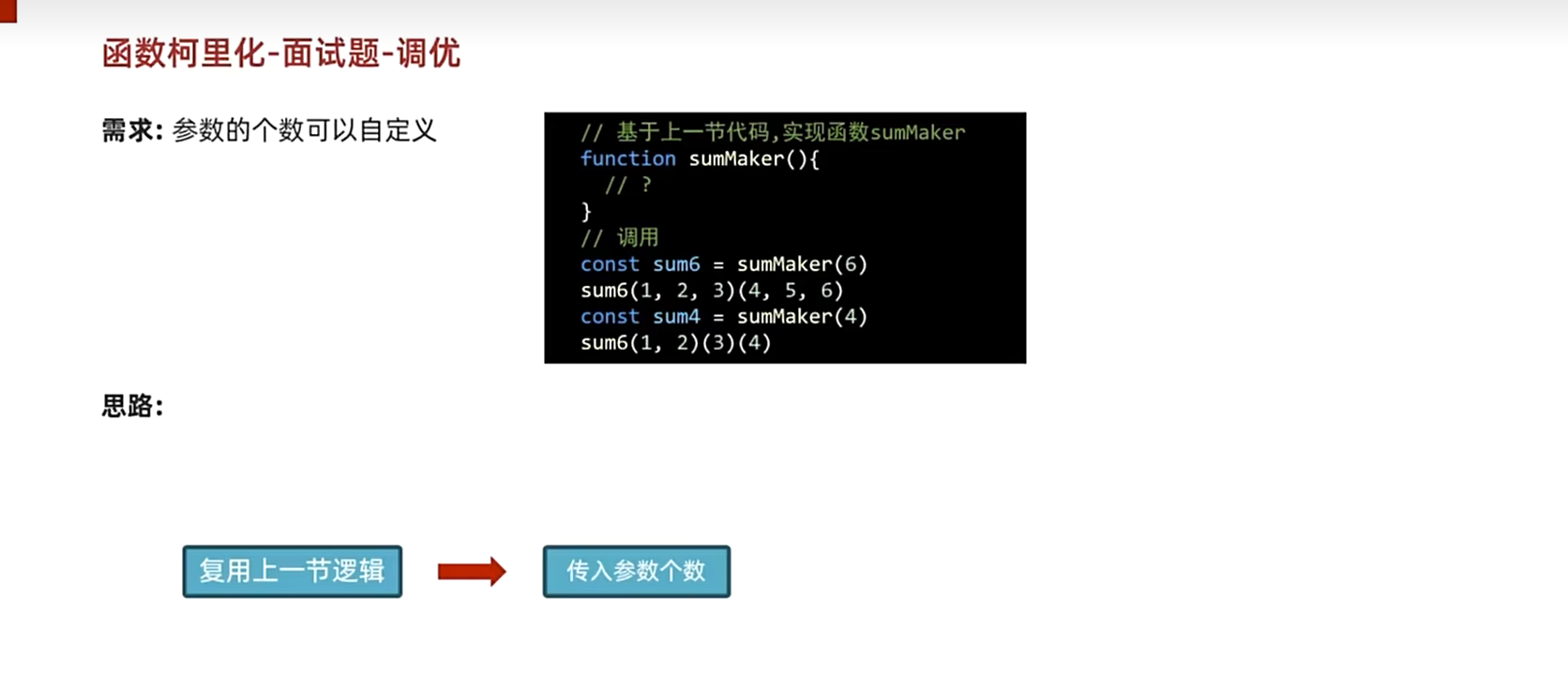
优化版本
js
function sumMaker(length) {
let nums = [];
function sum(...args) {
// @TODO
nums.push(...args);
if (nums.length >= length) {
const res = nums.slice(0, length).reduce((p, v) => p + v, 0);
nums = []; // 注意累加之后需要清空数组,保证下次累加的值是正确的
return res;
} else {
return sum;
}
}
return sum;
}
const sum6 = sumMaker(6);
sum6(1)(2)(3)(4)(5);
const sum4 = sumMaker(4);
sum4(1)(2)(3)(4);柯里化应用--判断类型
参数复用: 为函数预制通用参数,供给多次重复调用

js
const typeOfTest = function (type) {
return function (obj) {
// return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) === `[object ${type}]`
return typeof obj === type;
};
};
const typeOfTest = (type) => (thing) => typeof thing === type;
const isString = typeOfTest("string");
const isNumber = typeOfTest("number");
const isBoolean = typeOfTest("boolean");
const isUndefined = typeOfTest("undefined");
const isFunction = typeOfTest("function");
const isObject = (type) => (thing) =>
thing !== null && typeof thing === "object";14. 实现深拷贝
js
function cloneDeep(oldObj) {
// TODO
let newObj = Array.isArray(oldObj) ? [] : {};
for (let k in oldObj) {
if (typeof oldObj[k] === "object") {
newObj[k] = cloneDeep(oldObj[k]);
} else {
newObj[k] = oldObj[k];
}
}
return newObj;
}15. 最大并发数限制的请求调度器
js
16. 实现异步队列
js
17. 实现 LRU 缓存
js
18. 解析 URL 参数
js
function parseURLParams(url) {
// @TODO
const params = {};
// 提取URL中的查询字符串部分
const queryString = url.split("?")[1];
if (!queryString) return params;
// 分割参数
const pairs = queryString.split("&");
for (const pair of pairs) {
// 处理有等号和无等号的情况
const [key, value = ""] = pair.split("=");
// 解码URL编码的字符
params[decodeURIComponent(key)] = decodeURIComponent(value);
}
return params;
}
// 使用URLSearchParams API的简化版本
function parseURLParamsModern(url) {
const params = new URLSearchParams(url.split("?")[1]);
return Object.fromEntries(params.entries());
}19. 实现睡眠函数
js
function sleep(ms) {
// @TODO
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
}
// 使用示例
async function demo() {
console.log("开始");
await sleep(1000);
console.log("延迟1秒后");
}20. 实现数组原型方法
forEach
js
Array.prototype.myForEach = function (callback, thisArg) {
// @TODO
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
callback.call(thisArg, this[i], i, this);
}
};map
js
Array.prototype.myMap = function (callback, thisArg) {
const result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
result.push(callback.call(thisArg, this[i], i, this));
}
return result;
};filter
js
Array.prototype.myFilter = function (callback, thisArg) {
const result = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (callback.call(thisArg, this[i], i, this)) {
result.push(this[i]);
}
}
return result;
};21 jquery 渲染表格,模拟虚拟 DOM
html
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/1.10.0/jquery.min.js"></script>
<body>
<div id="container"></div>
<button id="change-btn">change</button>
<script>
var data = [
{
name: "张三",
age: 18,
sex: "男",
},
{
name: "李四",
age: 19,
sex: "男",
},
{
name: "王五",
age: 20,
sex: "男",
},
];
// 渲染函数*/
var render = function (data) {
// todo
var $container = $("#container");
// 清空容器
$container.empty();
// 使用字符串拼接创建整个表格
var tableHTML = "<table>";
// 添加表头
tableHTML +=
"<thead><tr><th>姓名</th><th>年龄</th><th>性别</th></tr></thead>";
// 添加表格内容
tableHTML += "<tbody>";
data.forEach(function (item, index) {
tableHTML += "<tr>";
tableHTML += "<td>" + item.name + "</td>";
tableHTML += "<td>" + item.age + "</td>";
tableHTML += "<td>" + item.sex + "</td>";
tableHTML += "</tr>";
});
tableHTML += "</tbody>";
tableHTML += "</table>";
// 将整个表格HTML添加到容器
$container.append(tableHTML);
};
$("#change-btn").click(function () {
data[0].name = "zhangsan";
data[1].age = 21;
render(data);
});
render(data);
</script>
</body>22 实现 (5).add(3).minus(2) ===> 输出 6
js
;(function(){
// 每一个方法执行完,都要返回Number这个类的实例,这样才可以继续调用
// Number类原型中的方法(链式写法)
function check(num){
num = Number(num)
return isNaN(num)?0: num
}
function add(num) {
num = check(num)
return this + num
}
function minus(num) {
num = check(num)
return this - num
}
Number.prototype.add = add
Number.prototype.minus = minus
}());
const res = (5).add(3).minus(2)
console.log(res)23 如何把一个字符串的大小写取反(大写变小写, 小写变大写, 例如 AbC 变为 aBc)
方法1:使用循环
遍历字符串中的每个字符,然后根据其是否为大写或小写来决定是转换为大写还是小写
js
const str = 'AbCdeeeEEf&&&'
const test = (str)=>{
let s = ''
for(let i = 0; i< str.length ; i++){
let item = str[i]
if (item === item.toUpperCase()) {
s += item.toLowerCase()
}else if(item === item.toLowerCase()) {
s += item.toUpperCase()
}else{
s += item
}
}
return s
}
const res = test(str)
console.log('res:', res)方法1:使用ASCII码值进行转换
另一种方法是基于字符的ASCII码值进行转换,这种方法在某些情况下也能工作,但不是最直观的方法
js
const str = 'AbCdeeeEEf'
const test = (str)=>{
let s = ''
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
const item = str[i];
const itemCharCode = item.charCodeAt()
if (itemCharCode >= 65 && itemCharCode<= 90 ) {
s += String.fromCharCode(itemCharCode + 32);
}
else if (itemCharCode >= 97 && itemCharCode<=122 ) {
s += String.fromCharCode(itemCharCode - 32);
}
else{
s += String.fromCharCode(itemCharCode)
}
}
return s
}
const res = test(str)
console.log('res:', res)24 实现一个$attr(name, value) 遍历
html
<body>
<div id="AA" class="box clearfix"></div>
<div myIn="1"></div>
<div class="box clearfix"></div>
<div name="BB"></div>
<div></div>
<div id="AA"></div>
<div myIn="1" class="clearfix"></div>
<div class="box"></div>
<div myIn="2"></div>
<div name="BB"></div>
<script>
/*
实现一个$attr(name, value) 遍历
属性为name
值为value的元素集合
例如如下示例
*/
function $attr(property, value) {
// =》获取当前页面中所有的标签
let elements = document.getElementsByTagName('*');
let arr = []
// [].forEach.call(elements, item={});
elements = Array.from(elements)// 把非数组转换为数组
elements.forEach(item => {
// 存储的是当前元素的property 对应属性值
const itemValue = item.getAttribute(property)
if (itemValue && itemValue.includes(value)) {
arr.push(item)
}
});
return arr
}
console.log( $attr('myIn', '1'))
</script>
</body>25 某公司1-12月数据销售额
js
/*
某公司1-12月数据销售额,存到一个对象里面
如下:{
1: 222,
2: 123,
5: 888
}
请把数据结构处理为如下结构:
[222, 123, null, null, 888,
null,null,null,null,null,null,null,]
*/
var obj = {
1: 222,
2: 123,
5: 888,
};
let arr = new Array(12).fill(null).map((item, index)=>{
return obj[index + 1]||null
})
console.log(arr)
// -------------------------
// var obj = {
// 1: 222,
// 2: 123,
// 5: 888,
// };
// obj.length = 13;
// let arr = Array.from(obj).splice(1).map(item=> {
// return typeof item === 'undefined'?null: item
// })
// console.log(arr)
// -------------------------
// var obj = {
// 1: 222,
// 2: 123,
// 5: 888,
// };
// let arr = new Array(12).fill(null)
// Object.keys(obj).forEach(item=>{
// arr[item - 1] = obj[item]
// })
// console.log(arr)26 给定两个数组, 写一个方法计算它们的交集
js
// 给定两个数组, 写一个方法计算它们的交集
let num1 = [1,2,2,1];
let num2 = [2, 2];
// => 输出结果 [2, 2]
let res = []
num1.forEach(i=>{
if (num2.includes(i)) {
res.push(i)
}
})
console.log(res)
// 给定两个数组, 写一个方法计算它们的交集
let num1 = [1,2,2,1];
let num2 = [2, 2];
// => 输出结果 [2, 2]
let res = []
for (let i = 0; i < num1.length; i++) {
const item1 = num1[i];
for (let j = 0; j < num2.length; j++) {
const item2 = num2[j];
if (item1 === item2) {
res.push(item1)
break
}
}
}
console.log(res)